
For instance, as already mentioned, individuals with blood type A produce antibodies against antigens that an individual does not have (Anti-B). * The ABO antigens are expressed by the H and ABO genes.Īntigens of red blood cells are also referred to as isoantigens/agglutinogens while the corresponding antibodies are also known as isoantibodies/agglutinins.īlood agglutination occurs when antigens on the surface of red cells are identified as being foreign. A good example of this is the production of Rhesus antibodies that are produced by Rhesus negative mothers in response to a Rhesus positive fetus.

* Given that Rh D is also an antigen, the presence of this antigen can trigger the production of antibodies. For this reason, they can receive blood from any of the other groups given that they do not have antibodies that will target the new blood cells. For an individual with blood type A, then they have anti-B antibodies in their serum/plasma.Īn individual with blood type B on the other hand will have anti-B antibodies in their serum while an individual with blood type O has both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in their plasma.īecause a person with blood type AB has both antigens, they do not have antibodies. However, these antibodies are not located on the surface of red cells. Given that an individual’s blood type is determined by the type of antigens on their red cells, there are antibodies to the antigens present. * Group O was initially known as blood group C. With regards to the ABO system of blood grouping, there are four main blood types that include A (group A have the A antigen on their red cells), B (group B have B antigen on their red cells), AB (Group AB have AB antigens on their red cells), O (lack the A and B antigens). In human beings, as is the case with other animals, it's the antigens that are expressed on the surface of their red cells that determine the blood group of an individual. * While only ABO and Rh blood groups systems are of clinical significance, studies have shown there to be 36 blood group systems. * While some people may have the gene responsible for encoding the D antigen, this does not necessarily mean that they are capable of producing the antigen. However, in the event that it's absent, then an individual is rhesus negative. If this large molecule (D) is present, then an individual is said to be rhesus positive (RhD positive). Here, a gene known as RhD is responsible for encoding the D antigen which is then located on the surface of red cells (on the cell membrane). Unlike ABO, the RH blood group consists of proteins.
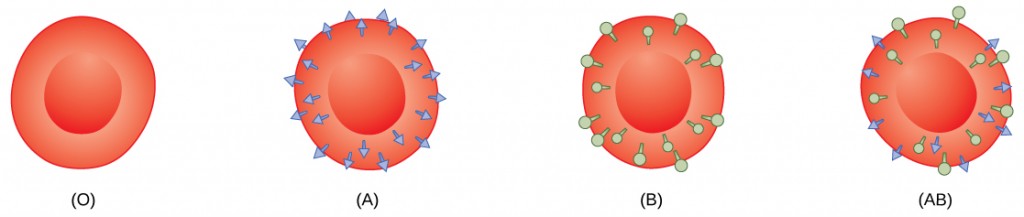
In particular, the DNA is involved in the production of given types of enzymes that catalyze the transfer of sugar units that form the antigens ABO.Īpart from these molecules (sugar units), the DNA is also involved in the production of another group known as the Rhesus (Rh) factor. As is the case with various other cellular components, the DNA is involved in the production of these molecules. Antigens (which consist of sugars or proteins) can be found on the surface of red blood cells and serve as a basis for blood grouping.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
